Parkinson’s disease is also called shaking palsy,was first described by James Parkinson in 1817.Parkinson’s disease occurs in elderly people due to idiopathic degeneration of Nigrostriatal system of dopaminergic neurons. There is a steady loss of dopamine and dopamine receptors with age in the basal ganglia in normal individuals, however it is markedly precipitated in individuals developing Parkinson’s disease.
Parkinson’s disease has both hypokinetic and hyperkinetic features. Parkinson disease is the first disease identified as being due to deficiency in a specific Neurotransmitter. It results from the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. The fibers to the part of the striatum are most severely affected.
The hypokinetic features of Parkinson disease are akinesia and Bradykinesia. The hyperkinetic features are cogwheel rigidity and tremor at rest.
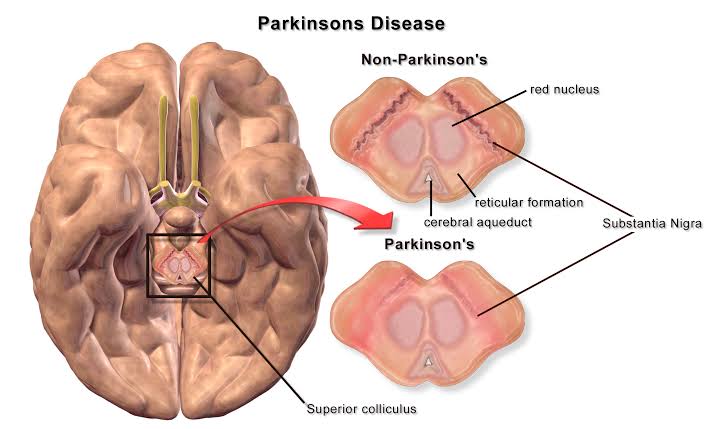
There are 7-10 million people worldwide in whom Parkinson disease has been diagnosed. The disease is 1.5 times more prevalent in men then in women. parkinsonism occurs in sporadic idiopathic form in many middle aged and elderly individuals and one of the most common Neurodegenerative diseases. It is estimated to occur in 1-2% of individuals over age of 65. Dopaminergic neurons and dopamine receptor are steadily lost with age in the basal ganglia in healthy individuals, and an acceleration of these losses apparently precipitates parkinsonism. Symptoms appear when 60-80% of the Nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons degenerate.
Sign & Symptoms
- There are three main symptoms;
- Tremor: shaking, which usually begins in the hand or arm and is more likely to occur when the limb is relaxed and resting.
- Slowest of movement (Bradykinesia).
- Muscle stiffness (Rigidity).

• OTHER PHYSICAL SYMPTOMS
- Balance problems.
- Loss of sense of smell.
- Nerve pain.
- Problems with peeing.
- Constipation.
- Erectile dysfunction.
- Sexual dysfunction.
- Dizziness,blurred vision.
- Excessive sweating.
- Swallowing difficulties.
- Excessive production of saliva(drooling).
- Insomnia.
•MENTAL SYMPTOMS
- Depression & Anxiety.
- Mild cognitive impairment.
- Dementia(visual hallucinations).
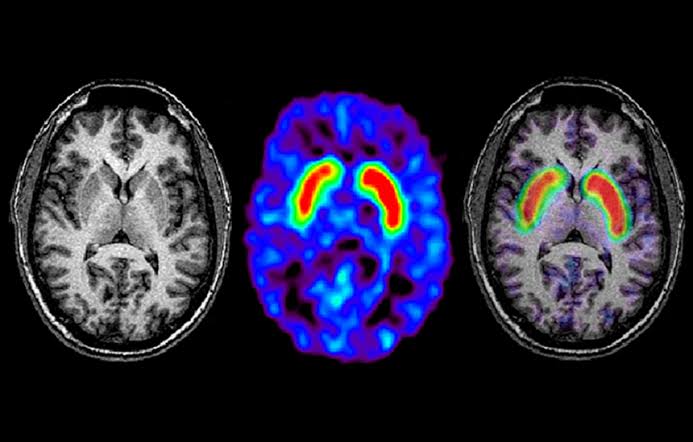
TREATMENT
- There is no cure for Parkinson disease, and drug therapies are designed to treat the symptoms.
- Sinemet, a combination of levodopa (L- dopa) and carbidopa, is the most commonly used drug for the treatment of Parkinson disease.
- The addition of carbidopa to levodopa increases its effectiveness and prevents the conversion of L-dopa to dopamine in the periphery and thus reduces some of the adverse side effects of levodopa, which includes; Nausea,vomit,and cardiac rhythm disturbances.
- Dopamine agonists, including apomorphine, bromocriptine,pramipexole and ropinirole,have also proven effective in some patients with Parkinson disease.
- Entacapone combination of L-dopa and cathechol-o-methyltransferase(COMT) inhibitor,are another class of drugs used to treat the disease.
- Drug dopamine is not used because it cannot cross the blood brain barrier.
- L-dopa in low doses diminishes rigidity and in high doses reduces tremors.
• Surgical destruction of the globus pallidus or ventrolateral nucleus of thalamus can also reform the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease by restoring the output balance towards normal.

